What is Task-Based Language Teaching?
Task-based language teaching (TBLT) refers to an approach based on the use of tasks as the
fundamental unit of planning and tutoring in language teaching. The main objective of TBLT
is to provide opportunities for the learners to experiment and explore both spoken and written
language through various learning activities. It aims to engage learners in the authentic,
practical, and purposeful use of language to achieve an outcome.

What is a task?
Task is a fundamental unit of planning and teaching. It is an activity or goal that is carried out
using language, such as finding a solution to a puzzle, taking part in role plays , reading a map
and giving directions, making a telephone call, writing a letter, or reading a set of instructions
, visiting a doctor, conducting an interview, or calling customer service for help. Engrossing
learners in task work provides a better context for the activation of learning processes. The
learners engage in naturalistic and meaningful communication.

Why do we use a task-based approach?
TBLT method is the most authentic, practical and learner centred second language teaching
approach. It has its roots in communicative language teaching. It is the only way that transforms
language learners into language users. Students gain confidence and fluency and make use of
the language the way they must do in the future. It effectively grooms the students to face real
time interviews and get employment. The basis of task-based syllabus for learners is the belief
that learning takes place through action, exploring different topics besides participating in
purposeful tasks. The activities of a task-based syllabus are done in a learning environment that
is stress-free and supportive for learners.

Classification of Tasks
Jigsaw tasks: combining different pieces of information to form a whole
Information-gap tasks: Completing an activity by finding out each other’s information.
Problem solving tasks: Arriving at a solution to the problem.
Decision making tasks: Choosing one possible outcome through discussion.
Opinion exchange tasks: Learners engage in discussion and exchange ideas.

Teacher Roles
Roles assumed for teachers:
Selector and sequence of tasks: selecting, adapting, and creating the tasks keeping with learner
needs
Preparing learners for tasks: providing partial demonstration of task procedures
Consciousness -raising employing form focussing techniques

Learner Roles
Primary roles that are implied by task work are:
Monitor: Students notice how language is used in communication
Risk taker and innovator: Learners create and interpret messages

The Role of Instructional Materials
Instructional materials play a significant role in TBLT as it is dependent on a sufficient supply
of appropriate classroom tasks. A wide variety realia can be used as a resource material which
include:
Realia-popular media products
Newspapers-determine sections like entertainment, job classified
Television-watching an infomercial, soap opera
Internet-comparative shopping analysis, search times

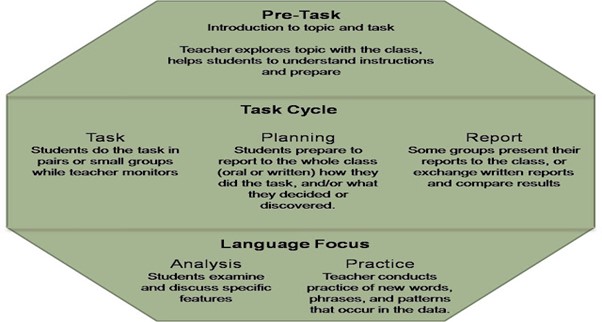
Procedure/Task activities designed
Pre-task activities: Teacher helps the students understand the theme and objectives of the task
Task activity: Students work in pairs with a task and hints
Post-task activity: Students listen to recordings of native speakers performing and what they
practiced and compare differences.
Conclusion
Task completion process is an effective learning practice and therefore students have the
ownership of their own learning. The teacher is a facilitator and overseer. TBLT approach is
more effective basis for instruction than any other teaching approaches.

FAQs
1) What is task-based language teaching?
2) How is TBLT used in English?
3) What are tasks in language learning?
